



NEXT GENERATION POLYURETHANE
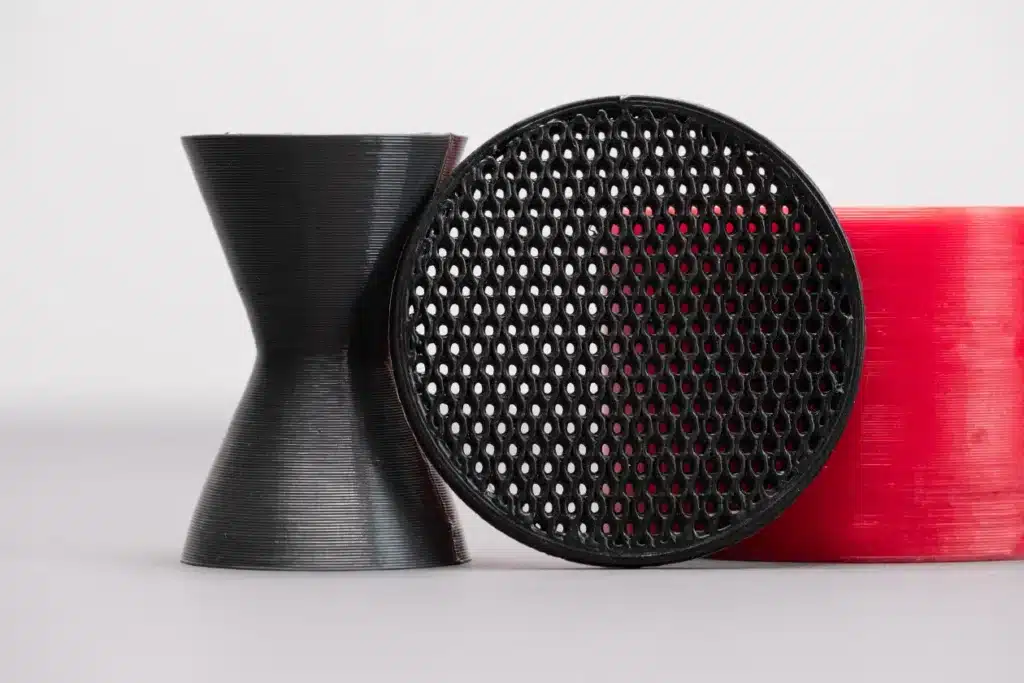
- Print unique shapes without the constraints imposed by the moulding process
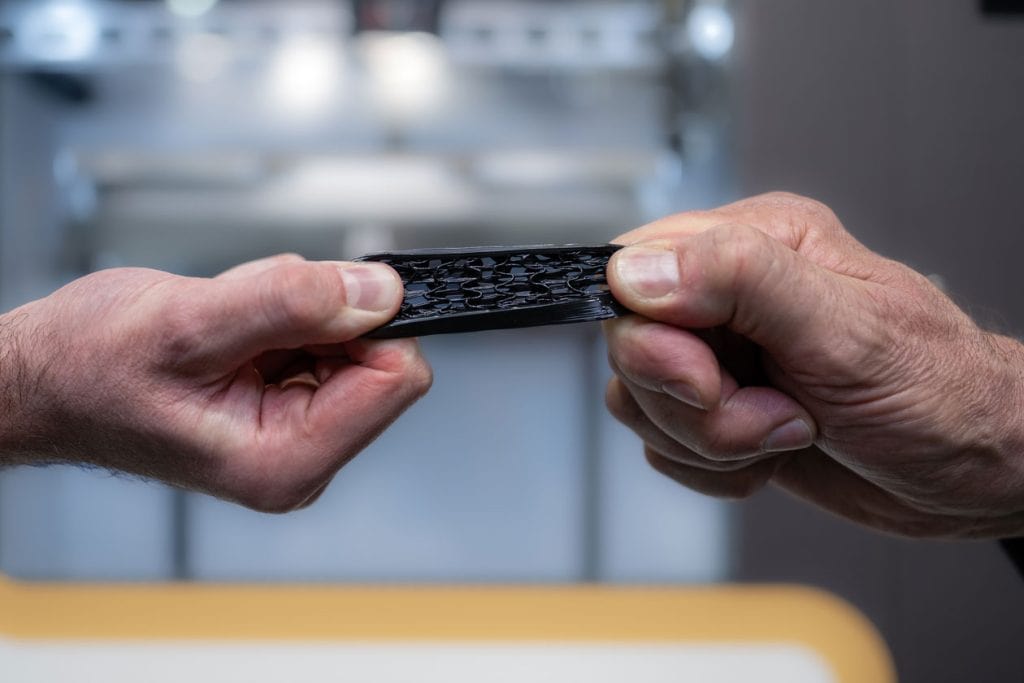
- As tough as vacuum casting PUs
- From soft to semi rigid with four different hardness levels available
- High mechanical and thermal resistance
space
space
- The SYNTHЭD+ PUprint line-up has the same very high mechanical and thermal properties as SYNTHENE’s elastomer range
- PUprint provides a sturdy alternative to the existing TPU filament materials
space
- Clients have already ordered the first 3D printers to print this cutting edge material with high demand from sectors like defence, aviation, automotive and other industries with high demands on quality
space
- PUprint is the first system to be launched in the SYNTHЭD+ range which will be dedicated to additive manufacturing
- SYNTHENE’s mindset is to bring high performance to the 3D printing industry for fully functional parts that are as resistant as conventionally produced parts
Documents
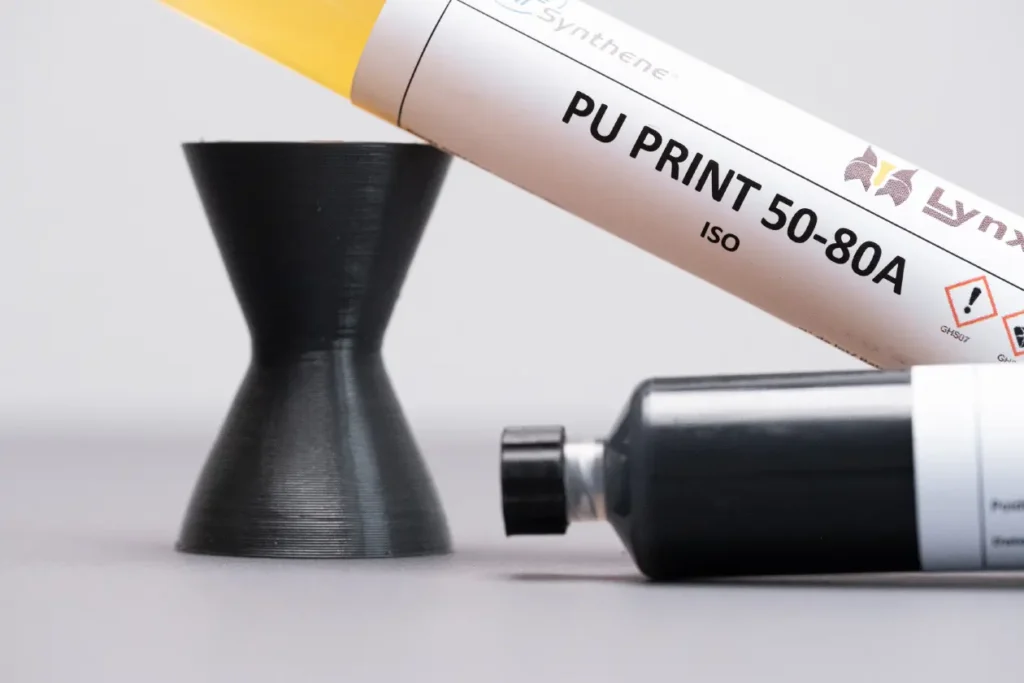
Management Summary RUBBER PUprint
Quick handout summarising the technical characteristics of SYNTHЭD+ PUprint, SYNTHENE’s first two-component polyurethane that can be 3D-printed.
fully functional 3D-printed parts
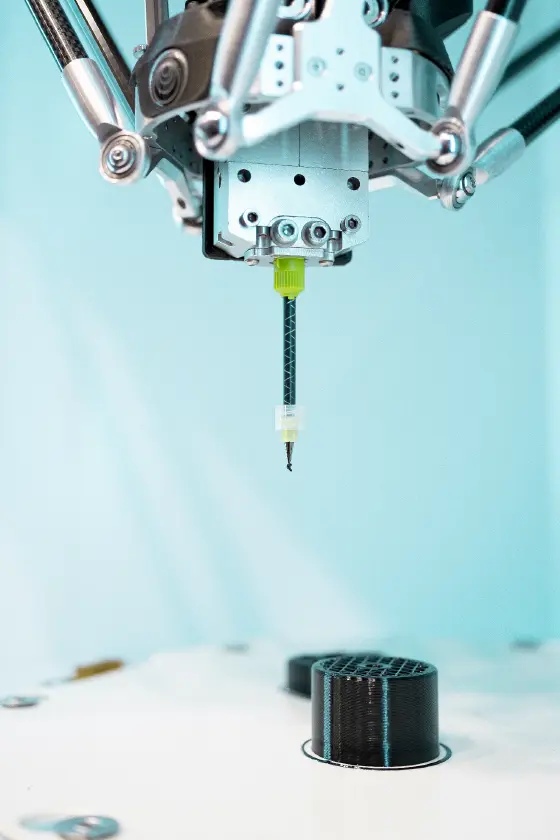
PRINT ANY SHAPE
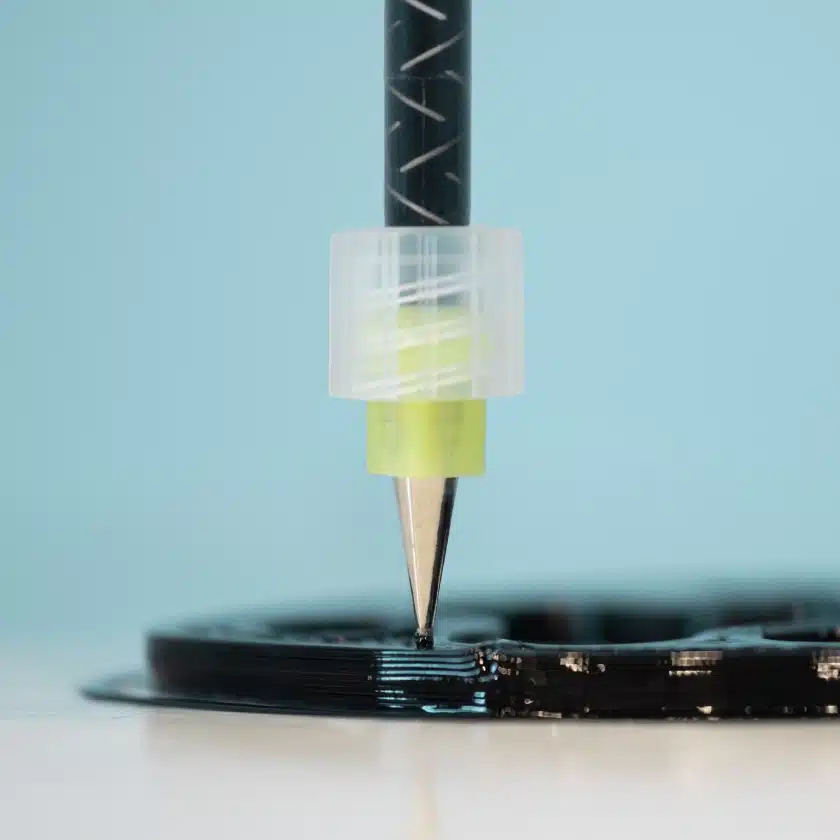
Any imaginable shaped object is 3D-printable with PUprint thanks to a specific formulation to produce high- precision parts.
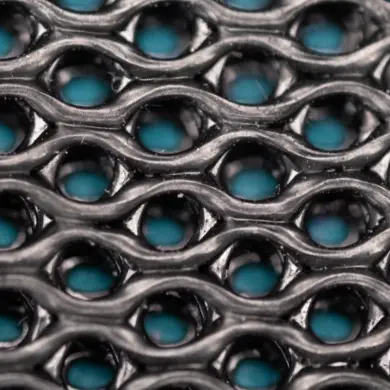
PRINT LIGHTER PIECES
By reducing the amount of filling the parts can become lighter and more flexible.
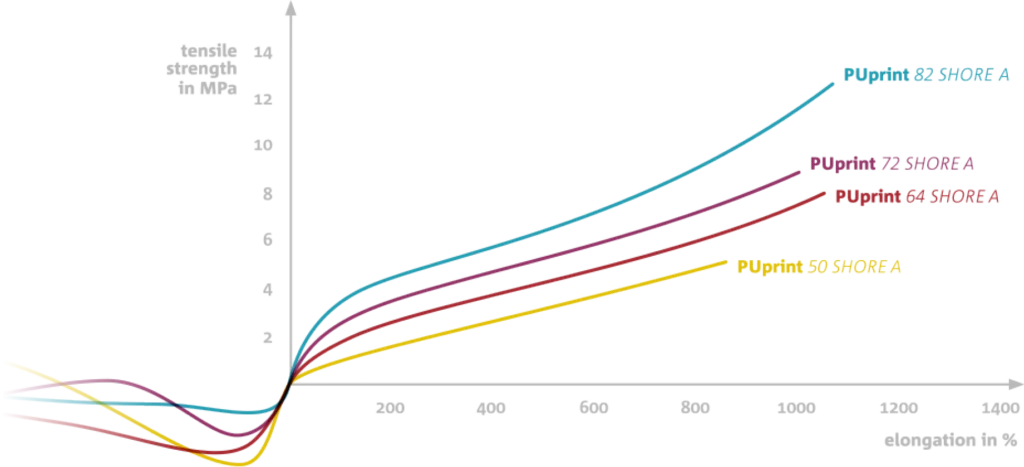
AS TOUGH AS VACUUM CASTING PU
The mechanical properties of SYNTHЭD+ PUprint are as good as of conventional PUs for vacuum casting.
HIGH THERMAL RESISTANCE
SYNTHЭD+ PUprint stands out with its high thermal resistance comparable to conventional industrial parts.

